What is cloud hosting How does cloud hosting work and how is the price of cloud hosting How are the prices determined How is the speed of cloud hosting websites? Moreover, we will know how cloud hosting servers work
We will discuss more Cloud hosting vs Shared hosting and Cloud hosting vs dedicated hosting, Which is better, and the Benefits of Cloud Hosting. SSD Hosting vs VPS Hosting
What is cloud hosting?
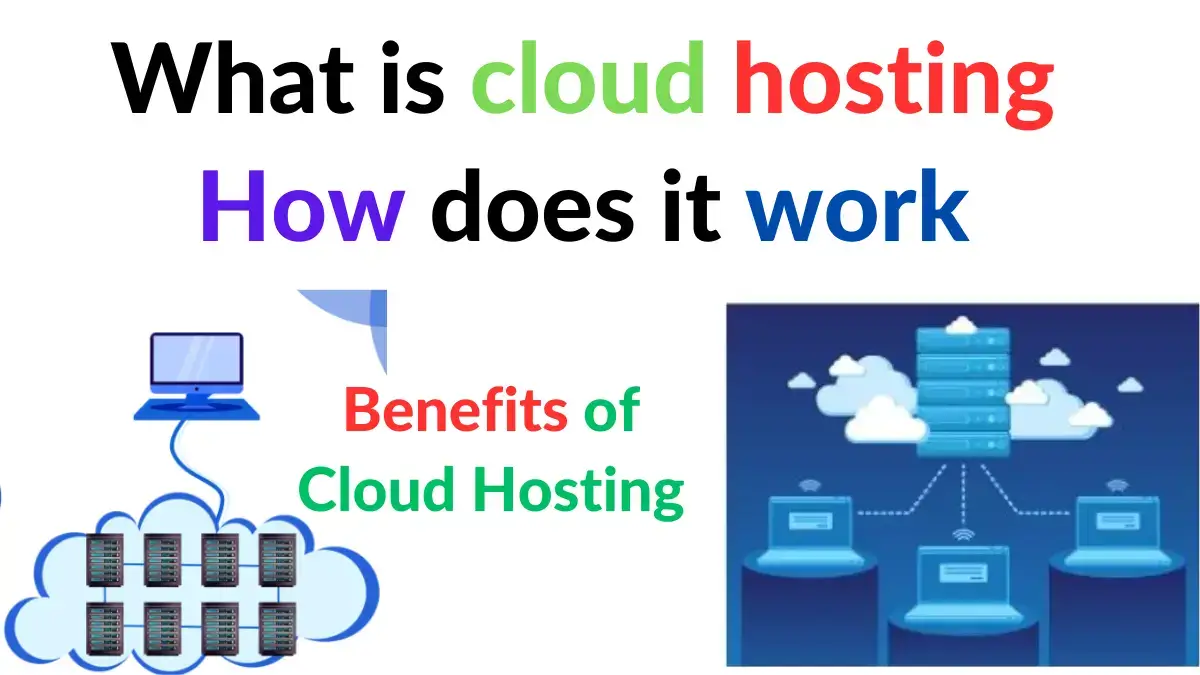
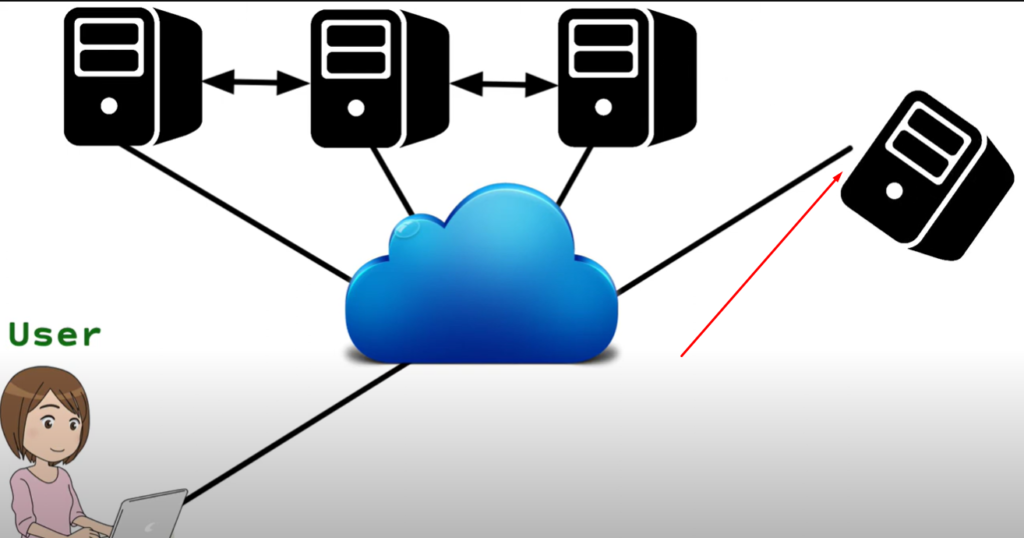
Cloud hosting is one of the types of web hosting. Cloud hosting is hosting that is connected to multiple servers, if one server drops, the website is connected to another server. So the websites of cloud hosting are very fast and the downtime of the website is much less.
Cloud hosting is not priced like regular hosting, Cloud hosting is priced based on how many GB of hosting a website visitor uses. Cloud hosting is priced depending on the visitor, So cloud hosting users have no fixed price limit for hosting per month
How does it work
Cloud hosting is associated with multiple servers, That is, cloud hosting is made up of many servers, When a website is linked to cloud hosting there is a problem with one of the servers in the cloud hosting. Then immediately the cloud hosting another server is connected to the website.
Cloud hosting vs dedicated hosting
This article lists the features of both cloud and dedicated server types and describes how they differ from one another. We give you all the information you require to choose the hosting solution that best suits your use case, financial constraints, and business requirements.
Servers in the Cloud
A virtual server operating in a cloud computing environment is called a cloud server. These servers offer unparalleled scalability (both up and down) and on-demand virtual resources to users.
Customers who use cloud servers don’t have to purchase or maintain any hardware. While customers customize virtual resources (processing, RAM, storage, etc.) to achieve the best configuration, the cloud provider takes care of maintenance.
A number of commercial advantages are provided by cloud servers, such as:
- No upfront purchases of hardware.
- instantaneous deployment of servers.
- a pay-per-use pricing system.
- elevated redundancy.
Many orchestration and automation possibilities are another benefit of virtualization, which is particularly useful for agile and DevOps teams.
Servers That Are Dedicated
A physical server used by one client and configured at a data center is called a dedicated server. These conventional systems, in contrast to cloud servers, rely on real hardware (CPUs, GPUs, RAM, hard drives, network cards, etc.) and do not use virtualization.
The entire device is yours to use when you set up a dedicated server. These servers are the fastest and safest hosting options available because you do not share resources with other users.
Among the many advantages of dedicated servers are:
- total freedom to alter the hardware and software setup.
- Superior data security and privacy are ensured by the single tenancy.
- elevated uptime levels.
- dependable quick loading speeds.
- Establishing a dedicated server gives you the option to:
A data center can rent you a server.
Install equipment that is privately owned at a data center run by a third party.
Benefits of Cloud Hosting
Flexible Pricing Structure: Regardless of whether you use all of the server resources or not, you pay a monthly fee with most other types of hosting. Paying only for what you use is possible with cloud hosting.
Therefore, you don’t need to fully increase your package if you anticipate a post becoming viral or if traffic to your website is exceptionally high. All you have to do is adjust your resources to match the spike in traffic and then reduce them when it settles down. Rather than requiring you to pay a flat hosting charge, your price is based on the total quantity of server resources that you use.
Very Easy to Scale Server Resources: It’s really simple to scale your server resources while using cloud hosting. You may examine your site’s performance in real-time with an easy-to-use site management dashboard available for the majority of cloud servers. You don’t have to wait for your hosting provider’s approval to scale server resources up or down.
High Uptime: The physical server environment determines how reliable your website is if you’re utilizing any type of traditional hosting. Your website also goes down if it does. Unless, of course, you’re using a CDN, which can assist in lowering the overall downtime of your website.
High uptime is a feature of cloud hosting architecture. Your website will be utilizing the resources of numerous servers virtually, so in the event that one goes down or has technical difficulties, you can easily switch to another server. Additionally, your website won’t crash from an unforeseen spike in traffic thanks to your capacity to grow server resources on demand.
cloud hosting vs shared hosting
shared hosting: The most popular and reasonably priced kind of hosting service is shared hosting. Several websites share one physical server’s space and resources when it comes to shared hosting. Because you get a whole server to yourself and don’t have to share its resources, cloud hosting is far more powerful. You are free to configure the server in different ways and to establish and manage hosting accounts.
Cloud hosting: If you require a more robust hosting solution for your website than shared hosting can offer, cloud hosting is an excellent choice. It is also incredibly versatile and strong. It offers you the option of autoscaling, which increases server resources in response to surges in traffic.